Researchers discover brain structure that helps us to understand what others think
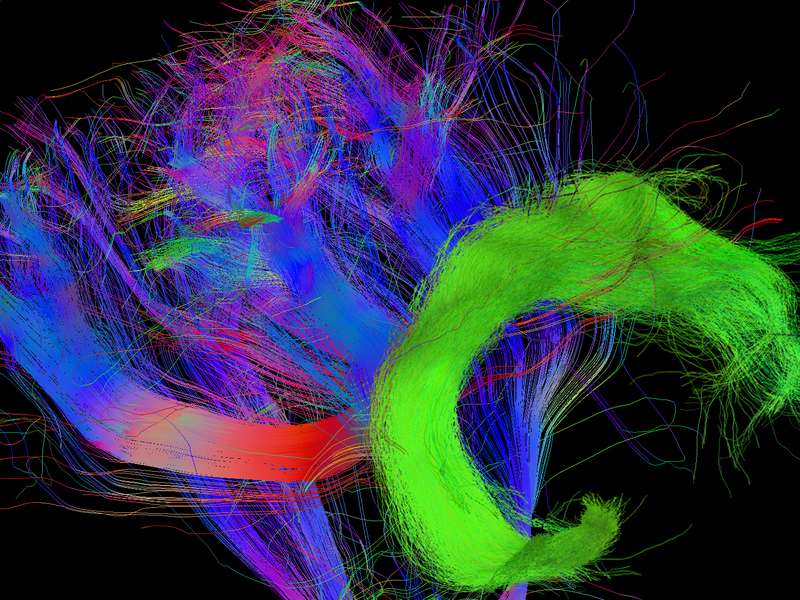
By the age of four years we suddenly start to understand what other people think and that their beliefs about the world might differ from our own. We then manage to do what 3-year-olds are not yet capable of – we can put ourselves in someone else's shoes. Researchers from the Max Planck Institute for Human Cognitive and Brain Sciences in Leipzig were able to show what supports this milestone in development: the maturation of a critical fibre connection in the brain.
If you tell a 3-year-old child the following story of little Maxi, they will most probably not understand: Maxi puts his chocolate on the kitchen table, then leaves to play outside. While he is gone, his mother puts the chocolate in the cupboard. Where will Maxi look for his chocolate? A 3-year-old child will not understand why Maxi would be surprised not to find the chocolate on the table where he left it. It is only by the age of 4 years that a child will correctly predict that Maxi will look for his chocolate where he left it and not in the cupboard where it is now.
Something similar can be observed when you show the 3-year-old child a chocolate box that contains pencils instead of chocolates. If you ask the child what another child would expect to be in the box, they will answer "pencils," although the other child would not know this. Only a year later, around the age of four years, however, they will understand that the other child had hoped for chocolates. Thus, there is a crucial developmental breakthrough between three and four years: This is when we start to attribute thoughts and beliefs to others and to understand that their beliefs can be different from ours. Before that age, thoughts don't seem to exist independently of what we see and know about the world. That is, this is when we develop a "Theory of Mind."
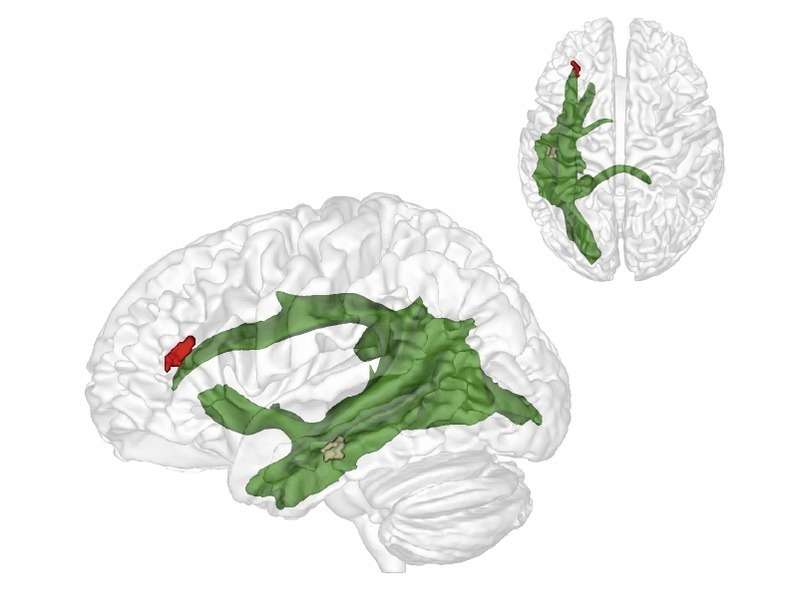
Researchers of the Max Planck Institute for Cognitive and Brain Sciences in Leipzig have now discovered what this developmental breakthrough is associated with. The maturation of fibres of a brain structure called the arcuate fascicle between the ages of three and four years establishes a connection between two critical brain regions: A region at the back of the temporal lobe that supports adults thinking about others and their thoughts and a region in the frontal lobe that is involved in keeping things at different levels of abstraction. It therefore helps us to understand what the real world is and what the thoughts of others are. Only when these two brain regions are connected through the arcuate fascicle can children start to understand what other people think. This is what allows us to predict where Maxi will look for his chocolate. Interestingly, this new connection in the brain supports this ability independently of other cognitive abilities, such as intelligence, language ability or impulse control.
"The strong arcuate fascicle might be the reason why humans are particularly good at understanding what other people think and predicting their actions," says the first author of the recently published article, Charlotte Grosse Wiesmann from the Max Planck Institute in Leipzig. "Although apes also seem to understand other individuals, they do this to a much lesser extent. This might result from the weaker fibre connection."
More information: Charlotte Grosse Wiesmann et al. White matter maturation is associated with the emergence of Theory of Mind in early childhood, Nature Communications (2017). DOI: 10.1038/ncomms14692



















