Abstract
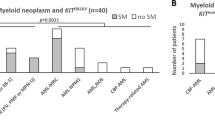
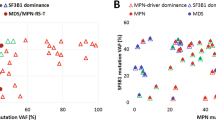
Myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS) and chronic myelomonocytic leukemia (CMML) are reported in up to 20% patients with blastic plasmacytoid dendritic cell neoplasm (BPDCN), where a shared clonal origin is shown in individual case studies. In this study, we performed targeted next generating sequencing on multiple bone marrow (BM), skin or sorted cells from 51 BPDCN patients (68.7 years,14.4–84.7), and detected mutations in BM hematopoietic cells in 65% (30/46) and BPDCN in 100% (27/27), both components showing similar high frequencies of TET2 (60% versus 58%) and ASXL1 (33% versus 40%). Of 24 patients with paired mutation data, 13(54%) had shared mutations, with TET2(77%), ASXL1(37%) and ZRSR2(22%) the most commonly shared, and NRAS the most gained mutation in BPDCN(9/24, 38%). Karyotypic abnormalities were detected in 19/29(66%) BPDCN but only in 1/49 BM hematopoietic cells, providing additional evidence of clonal evolution. BM clonal hematopoiesis (CH) was associated with an older age (p < 0.001), being confounding factors in multivariate analysis; whereas <10% BM BPDCN infiltrate and stem cell transplant were associated with favorable outcomes. This study is the first to report a high prevalence of BM CH in BPDCN patients beyond an associated diagnosis of MDS/CMML, and demonstrates a frequent clonal relationship in elderly, findings contributing to the understanding of BPDCN clonal origin.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rodrigues PF, Alberti-Servera L, Eremin A, Grajales-Reyes GE, Ivanek R, Tussiwand R. Distinct progenitor lineages contribute to the heterogeneity of plasmacytoid dendritic cells. Nat Immunol. 2018;19:711–22.
Chaperot L, Bendriss N, Manches O, Gressin R, Maynadie M, Trimoreau F, et al. Identification of a leukemic counterpart of the plasmacytoid dendritic cells. Blood. 2001;97:3210–7.
Laribi K, Denizon N, Besancon A, Farhi J, Lemaire P, Sandrini J, et al. Blastic plasmacytoid dendritic cell neoplasm: from origin of the cell to targeted therapies. Biol Blood Marrow Transpl. 2016;22:1357–67.
Sapienza MR, Pileri A, Derenzini E, Melle F, Motta G, Fiori S, et al. Blastic plasmacytoid dendritic cell neoplasm: state of the art and prospects. Cancers. 2019;11:595.
Sapienza MR, Fuligni F, Agostinelli C, Tripodo C, Righi S, Laginestra MA, et al. Molecular profiling of blastic plasmacytoid dendritic cell neoplasm reveals a unique pattern and suggests selective sensitivity to NF-kB pathway inhibition. Leukemia. 2014;28:1606–16.
Cota C, Vale E, Viana I, Requena L, Ferrara G, Anemona L, et al. Cutaneous manifestations of blastic plasmacytoid dendritic cell neoplasm-morphologic and phenotypic variability in a series of 33 patients. Am J Surg Pathol. 2010;34:75–87.
Pagano L, Valentini CG, Pulsoni A, Fisogni S, Carluccio P, Mannelli F, et al. Blastic plasmacytoid dendritic cell neoplasm with leukemic presentation: an Italian multicenter study. Haematologica. 2013;98:239–46.
Tang Z, Tang G, Wang SA, Lu X, Young KH, Bueso-Ramos CE, et al. Simultaneous deletion of 3’ETV6 and 5’EWSR1 genes in blastic plasmacytoid dendritic cell neoplasm: case report and literature review. Mol Cytogenet. 2016;9:23.
Leroux D, Mugneret F, Callanan M, Radford-Weiss I, Dastugue N, Feuillard J, et al. CD4(+), CD56(+) DC2 acute leukemia is characterized by recurrent clonal chromosomal changes affecting 6 major targets: a study of 21 cases by the Groupe Francais de Cytogenetique Hematologique. Blood. 2002;99:4154–9.
Alayed K, Patel KP, Konoplev S, Singh RR, Routbort MJ, Reddy N, et al. TET2 mutations, myelodysplastic features, and a distinct immunoprofile characterize blastic plasmacytoid dendritic cell neoplasm in the bone marrow. Am J Hematol. 2013;88:1055–61.
Stenzinger A, Endris V, Pfarr N, Andrulis M, Johrens K, Klauschen F, et al. Targeted ultra-deep sequencing reveals recurrent and mutually exclusive mutations of cancer genes in blastic plasmacytoid dendritic cell neoplasm. Oncotarget. 2014;5:6404–13.
Menezes J, Acquadro F, Wiseman M, Gomez-Lopez G, Salgado RN, Talavera-Casanas JG, et al. Exome sequencing reveals novel and recurrent mutations with clinical impact in blastic plasmacytoid dendritic cell neoplasm. Leukemia. 2014;28:823–9.
Pagano L, Valentini CG, Grammatico S, Pulsoni A. Blastic plasmacytoid dendritic cell neoplasm: diagnostic criteria and therapeutical approaches. Br J Haematol. 2016;174:188–202.
Batta K, Bossenbroek HM, Pemmaraju N, Wilks DP, Chasty R, Dennis M, et al. Divergent clonal evolution of blastic plasmacytoid dendritic cell neoplasm and chronic myelomonocytic leukemia from a shared TET2-mutated origin. Leukemia. 2021;35:3299–303.
Brunetti L, Di Battista V, Venanzi A, Schiavoni G, Martelli MP, Ascani S, et al. Blastic plasmacytoid dendritic cell neoplasm and chronic myelomonocytic leukemia: a shared clonal origin. Leukemia. 2017;31:1238–40.
Patnaik MM, Lasho T, Howard M, Finke C, Ketterling RL, Al-Kali A, et al. Biallelic inactivation of the retinoblastoma gene results in transformation of chronic myelomonocytic leukemia to a blastic plasmacytoid dendritic cell neoplasm: shared clonal origins of two aggressive neoplasms. Blood Cancer J. 2018;8:82.
Wang W, Khoury JD, Miranda RN, Jorgensen JL, Xu J, Loghavi S, et al. Immunophenotypic characterization of reactive and neoplastic plasmacytoid dendritic cells permits establishment of a 10-color flow cytometric panel for initial workup and residual disease evaluation of blastic plasmacytoid dendritic cell neoplasm. Haematologica. 2021;106:1047–55.
Sukswai N, Aung PP, Yin CC, Li S, Wang W, Wang SA, et al. Dual expression of TCF4 and CD123 is highly sensitive and specific for blastic plasmacytoid dendritic cell neoplasm. Am J Surg Pathol. 2019;43:1429–37.
Loghavi S, DiNardo CD, Furudate K, Takahashi K, Tanaka T, Short NJ, et al. Flow cytometric immunophenotypic alterations of persistent clonal haematopoiesis in remission bone marrows of patients with NPM1-mutated acute myeloid leukaemia. Br J Haematol. 2021;192:1054–63.
Luthra R, Patel KP, Reddy NG, Haghshenas V, Routbort MJ, Harmon MA, et al. Next-generation sequencing-based multigene mutational screening for acute myeloid leukemia using MiSeq: applicability for diagnostics and disease monitoring. Haematologica. 2014;99:465–73.
Morita K, Wang F, Jahn K, Hu T, Tanaka T, Sasaki Y, et al. Clonal evolution of acute myeloid leukemia revealed by high-throughput single-cell genomics. Nat Commun. 2020;11:5327.
Richards S, Aziz N, Bale S, Bick D, Das S, Gastier-Foster J, et al. Standards and guidelines for the interpretation of sequence variants: a joint consensus recommendation of the American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics and the Association for Molecular Pathology. Genet Med. 2015;17:405–24.
Hirsch CM, Nazha A, Kneen K, Abazeed ME, Meggendorfer M, Przychodzen BP, et al. Consequences of mutant TET2 on clonality and subclonal hierarchy. Leukemia. 2018;32:1751–61.
Jaiswal S, Fontanillas P, Flannick J, Manning A, Grauman PV, Mar BG, et al. Age-related clonal hematopoiesis associated with adverse outcomes. N Engl J Med. 2014;371:2488–98.
Bick AG, Weinstock JS, Nandakumar SK, Fulco CP, Bao EL, Zekavat SM, et al. Inherited causes of clonal haematopoiesis in 97,691 whole genomes. Nature. 2020;586:763–8.
Elena C, Galli A, Such E, Meggendorfer M, Germing U, Rizzo E, et al. Integrating clinical features and genetic lesions in the risk assessment of patients with chronic myelomonocytic leukemia. Blood. 2016;128:1408–17.
Itzykson R, Kosmider O, Renneville A, Gelsi-Boyer V, Meggendorfer M, Morabito M, et al. Prognostic score including gene mutations in chronic myelomonocytic leukemia. J Clin Oncol. 2013;31:2428–36.
Summerer I, Walter W, Meggendorfer M, Kern W, Haferlach T, Haferlach C, et al. Comprehensive analysis of the genetic landscape of 21 cases with blastic plasmacytoid dendritic cell neoplasm by whole genome and whole transcriptome sequencing. Leuk Lymphoma. 2021;62:2543–6.
Mason CC, Khorashad JS, Tantravahi SK, Kelley TW, Zabriskie MS, Yan D, et al. Age-related mutations and chronic myelomonocytic leukemia. Leukemia. 2016;30:906–13.
Steensma DP, Bejar R, Jaiswal S, Lindsley RC, Sekeres MA, Hasserjian RP, et al. Clonal hematopoiesis of indeterminate potential and its distinction from myelodysplastic syndromes. Blood. 2015;126:9–16.
Liao C, Hu NX, Song H, Zhang JY, Shen DY, Xu XJ, et al. Pediatric blastic plasmacytoid dendritic cell neoplasm: report of four cases and review of literature. Int J Hematol. 2021;113:751–9.
Pemmaraju N, Lane AA, Sweet KL, Stein AS, Vasu S, Blum W, et al. Tagraxofusp in blastic plasmacytoid dendritic-cell neoplasm. N Engl J Med. 2019;380:1628–37.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
MK, SAW, CCY, GT, IB, WW, SK, and CL: data collection and analysis, figures and tables. MK, KT, JDK, SL, CCY, WW, and SAW: NGS testing, interpretation and flow cytometry analysis. NP and KT: clinical data, treatment and clinical outcome analysis. SAW, MK, and LJM: manuscript writing. SAW, JDK, NP, and LJM: experiment design. All authors have read and approved the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Khanlari, M., Yin, C.C., Takahashi, K. et al. Bone marrow clonal hematopoiesis is highly prevalent in blastic plasmacytoid dendritic cell neoplasm and frequently sharing a clonal origin in elderly patients. Leukemia 36, 1343–1350 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41375-022-01538-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41375-022-01538-9
This article is cited by
-
Genome-wide DNA methylation-analysis of blastic plasmacytoid dendritic cell neoplasm identifies distinct molecular features
Leukemia (2024)
-
Diagnostic management of blastic plasmacytoid dendritic cell neoplasm (BPDCN) in close interaction with therapeutic considerations
Annals of Hematology (2024)
-
Ultraviolet radiation shapes dendritic cell leukaemia transformation in the skin
Nature (2023)
-
Coincidence of cutaneous blastic plasmacytoid dendritic cell neoplasm and myelodysplastic syndrome derived from clonal hematopoiesis
Blood Cancer Journal (2023)
-
Top Ten Lymphoproliferative Lesions Not to Miss When Evaluating Oral Ulcer Biopsies
Head and Neck Pathology (2023)