This Dr. Axe content is medically reviewed or fact checked to ensure factually accurate information.
With strict editorial sourcing guidelines, we only link to academic research institutions, reputable media sites and, when research is available, medically peer-reviewed studies. Note that the numbers in parentheses (1, 2, etc.) are clickable links to these studies.
The information in our articles is NOT intended to replace a one-on-one relationship with a qualified health care professional and is not intended as medical advice.
This article is based on scientific evidence, written by experts and fact checked by our trained editorial staff. Note that the numbers in parentheses (1, 2, etc.) are clickable links to medically peer-reviewed studies.
Our team includes licensed nutritionists and dietitians, certified health education specialists, as well as certified strength and conditioning specialists, personal trainers and corrective exercise specialists. Our team aims to be not only thorough with its research, but also objective and unbiased.
The information in our articles is NOT intended to replace a one-on-one relationship with a qualified health care professional and is not intended as medical advice.
Organic Farming: 5 Major Benefits (Plus, Can It Really Feed the World?)
September 25, 2017

Did you know it’s possible to produce healthy crops without the use of preservatives, radiation, genetic modification, sewage sludge, synthetic fertilizers and chemical pesticides? People practicing organic farming know it’s true. And so does a growing portion of the U.S. population. So what’s the benefit of organic? First and foremost, organic farmers keep nasty and unhealthy things commonly found in conventional farming out of farm fields and the crops we eat.
A 2014 Gallup poll found that 45 percent of Americans seek out organic foods, while 15 percent actually actively avoid them. (1) But let’s take a step back. What is organic? And why are people buying it in unprecedented numbers? The organic definition is: relating to or derived from living matter. Organic food comes from organic farming. In the United States, the United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) certifies whether or not a farm or a product is truly organic.
According to USDA, “Organic food is produced without using most conventional pesticides; fertilizers made with synthetic ingredients or sewage sludge; bioengineering; or ionizing radiation. Before a product can be labeled ‘organic,’ a Government-approved certifier inspects the farm where the food is grown to make sure the farmer is following all the rules necessary to meet USDA organic standards. Companies that handle or process organic food before it gets to your local supermarket or restaurant must be certified, too.” (2)
You may already be eating organic food, but do you know the answer to the following question: What are the benefits of organic farming? I’m about to tell you that and so much more. Organic farming facts are so intriguing; in fact, if you want to know how to start organic farming today, it’s really not as hard as you might think!
What Is Organic Farming? Current Standards
By definition, what is organic agriculture? After a few years of work, IFOAM — the International Federation of Organic Agriculture Movements — came up with the following definition for organic agriculture: (3)
“Organic Agriculture is a production system that sustains the health of soils, ecosystems and people. It relies on ecological processes, biodiversity and cycles adapted to local conditions, rather than the use of inputs with adverse effects. Organic Agriculture combines tradition, innovation and science to benefit the shared environment and promote fair relationships and a good quality of life for all involved.”
In general, organic farming is comprised of several key aspects, including the use of natural fertilizers like compost and manure. Crop rotation, companion planting and natural pest control are other hallmarks of organic farming. Unlike conventional farming, organic farming grows organic food without relying on harmful synthetic, chemical substances.
There are strict standards and inspections when it comes to the production and processing of organic food. The term “100 percent orgacnic” is used for certified organically farmed produce. USDA certified organic vegetables, fruits, eggs, meats and any other one-ingredient foods are typically labeled “100 percent organic.” Food products that have multiple ingredients can also be labeled as “100 percent organic” or they can be “certified USDA organic,” as long as they use a minimum of 95 percent organic ingredients. In order for a product to say that it is “made with organic ingredients” then it needs to have at least 70 percent organic ingredients. (4) Since the products of organic farming are known as a single ingredient, they are either completely organic or not, there’s no in between.
Is there anything done to prevent farmers and companies from falsely labeling food as organic? Anyone caught selling or even just labeling a product “organic” when it doesn’t meet USDA standards can be charged a fine of up to $11,000 for each violation. (5) The USDA also clearly states, “No matter where it was grown, if a product has the USDA Organic label on it, it wasn’t produced with GMOs.” (6)
Organic Soil
As you might expect, organic farmers use organic soil. In general, soil is a complex mixture of minerals, organic matter, water and air. By nature, soil is natural and made up of organic matter. So what’s the difference between organic soil and non-organic soil? Organic vs. nonorganic soil differs in the way the soil is maintained. Nonorganic or conventional farmers us synthetic fertilizers, pesticides and other unnatural additions to their soil in order to fight off pests and disease, and to maximize the growth of crops. Meanwhile, organic soil is only maintained with the use of of natural materials to foster growth and deal with unwanted guests. (7)
Organic Fertilizer for Weed Management
When comparing organic farming vs. conventional farming, one of the clearest differences is how each method of farming deals with pests and unwanted weeds. One of the best methods to discourage weed growth is crop rotation. Farmers that continue to grow the same exact crop over and over in the same place actually give weeds an advantage. When crops are rotated, then it’s much harder for weeds to thrive. (8)
Other organic weed management techniques include weeding by hand, using mechanical weeders, green manures, planting crops closely and leaving as little space as possible and letting animals eat the weeds as they like.
Organic Pesticides
If you’re eating organic foods, it doesn’t mean pesticides were never used during their growing period, but it does mean that they are free from conventional or synthetic pesticides. If pesticides are used on organic foods, they are typically made from natural ingredients. However, even some natural substances (such as arsenic and tobacco dust) are not allowed because they’re known to have negative impacts on health. (9, 10)
No Genetic Modification
One of the most important organic farming facts involves GMOs. Certified organic farmers can never grow or sell genetically modified foods. In the exact words of the USDA:
“The use of genetic engineering, or genetically modified organisms (GMOs), is prohibited in organic products. This means an organic farmer can’t plant GMO seeds, an organic cow can’t eat GMO alfalfa or corn, and an organic soup producer can’t use any GMO ingredients. To meet the USDA organic regulations, farmers and processors must show they aren’t using GMOs and that they are protecting their products from contact with prohibited substances, such as GMOs, from farm to table.” (11)
Organically Fed Livestock
Like other organic products, organic livestock can only eat 100 percent certified organic feed. The only thing they are allowed other than organic feed are some vitamins and minerals so they can fulfill their daily nutritional requirements. Similar to organic produce, organic livestock must also be produced without the use of sewage sludge, genetic modification or ionizing radiation. (12)
If you’re looking for organic farming examples, the USDA also maintains a list of certified organic farms and businesses in the United Sates at theOrganic Integrity Database.
History of Organic Farming
Conventional farming has turned into very big business. “Giant agribusiness corporations” are driving out many smaller farms, making it extremely difficult for small farmers to survive. These corporate farms are less in touch with the land, are more reliant on chemicals and are even genetically modifying crops. While it may be said that it’s all in the interest in keeping up with population growth, you have to wonder what is being lost as farming becomes less and less what it once was.
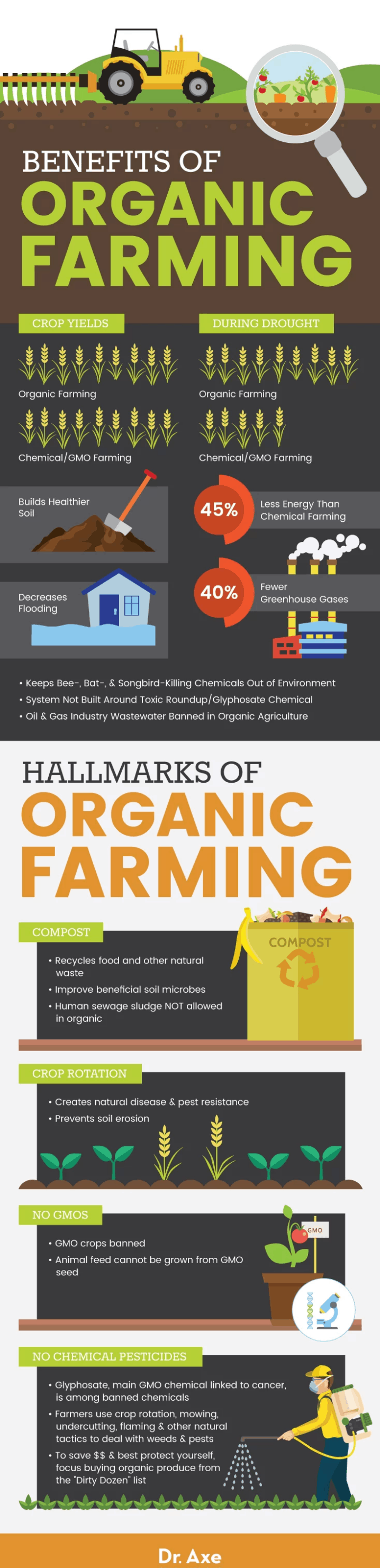
The Rodale Institute’s 30-Year Farming Systems Trial provides data showing that organic crop production actually matches chemical agriculture yields. In fact, in years of drought (which is becoming more common), organic actually outperforms chemical ag, all while building up the soil instead of depleting it. (Think of healthy, microbial-rich organic soil as a sponge that is better equipped to store water.) Other findings?
- Organic farming is more efficient and uses 45 percent less energy than chemical farming
- Organic farming produces 40 percent less greenhouse gas emissions
- Organic farming is more profitable than chemical-based farming
Organic farming methods aren’t exactly something new, but organic farming as an “alternative agricultural system” is something that began in the early 20th century as a response to all of these major changes to the world of farming I just mentioned. (13)
For thousands of years, “traditional farming” took place around the world and the farming methods used were organic. You could say that organic farming is really going back to the roots of farming, literally. (14)
The United State’s 1990 Farm Bill put into place The Organic Foods Production Act (OFPA). This is a significant landmark in organic farming in the U.S., since OFPA enacted national standards by which foods could carry organic labeling. The act also created the USDA National Organic Program (NOP), which clarified how organically grown foods needed to be grown, handled and processed. (15)
Fast forward to present day and organic farming is now taking place all over the world. It’s estimated that at least 160 countries are currently practicing organic agriculture. The market for organic products is strongest in North America and Europe, while Australia is said to have the largest amount of land dedicated to organic farming. India actually has the highest number of organic producers. (16)
What is organic farming in India? Organic farming is becoming more and more important in India as the country realizes the devastating effects of conventional farming. Most concerning is the recent designation of the Punjab’s Malwa region as the “cancer belt” of India. An alarming number of people have been stricken with cancer; it’s associated with cotton farmers’ overuse of conventional pesticides. It’s not to say that organic farming is a new concept in India, but its value is certainly increasing in recent times. More people in India are now turning to organic farming as a sustainable agribusiness that uses fertilizers created from local, natural ingredients, along with natural pesticides that are sprayed according to the moon’s movements. Overall, people in India are learning that organic gardening doesn’t only mean no more toxic chemicals, it also means a way to provide delicious food for themselves and their loves ones, as well as a way to make a living. (17)
Key Principles of Organic Farming
The following are some of the most fundamental aspects of organic farming:
Compost
Compost, also known as “black gold,” is a vital part of organic farming and a key ingredient in hearty, organic soil. What is compost? Compost can be defined as organic matter that has been decomposed and recycled to be used as an addition and enhancer to soil. At its best and when done right, compost is a way to really boost the nutrient content and quality of soil.
There’s a good reason why the absence of sewage sludge is a major positive aspect of organic farming. Some companies are marketing compost and potting soil amendments as “organic” when it’s really human sewage sludge in compost. Not only does this sludge contain human waste, but it also contains everything else that goes down the drain which is often a whole lot of toxic chemicals from various products. Luckily, this is banned in organic agriculture. (18)
For more info on how to compost in a healthy, sludge-free way, check out: DIY Compost: Simple Steps to Make ‘Black Gold’ at Home
Crop Rotation
Crop rotation is an important part of organic farming for multiple reasons. When farmers grow the same crops in the same location year after year (this is called monoculture), it negatively affects the health of soil. Crop rotation is much healthier for the land than monoculture. What is crop rotation? Crop rotation involves a farmer growing a different type of crop in the same area of the land each growing season. (19)
Crop rotation is a natural way for organic farmers to reduce pests, weeds and soil diseases. It’s also a way to avoid depleting the soil’s nutrients, which means more fertile soil and better crop production. Crop rotation also aids in the reduction of soil erosion, something more and more important as floods and flood damage is becoming a more prevalent and expensive problem for society. (20)
Companion Planting
Companion plant is another aspect of organic farming. Companion planting is when one type of plant is purposely planted near another because they grow well together. Apparently, some plants just make better neighbors. Organic farmers and gardeners make a point to know the best companions before they start planting. For example, planting basil and dill near tomatoes can protect them from unwanted tomato hornworms, which are one of the most destructive pests of tomato, potato, eggplant and pepper plants. (21) There are also a number of plants you should NOT grow next to each other.
Here are some great organic farming articles for beginners (or anyone interested in organic farming):
- How to Start an Organic Farm
- Starting an Organic Farm or Ranch
- Considerations for a Beginning Organic Farmer
5 Major Benefits of Organic Farming
These are just some of the top benefits of organic farming:
1. Healthier, More Nutritious Foods
In general, certified organic produce is grown without the following: preservatives, radiation, genetic modification, sewage sludge, synthetic fertilizers, and chemical pesticides. (22) We now know that there are certain nonorganic produce items that are especially loaded with pesticides. This group of fruits and vegetables are typically referred to as the Dirty Dozen. If you can only afford to buy some organic produce, then these are definitely the 12 to put on your organic shopping list.
According to a 2014 study published in The British Journal of Nutrition, organic crops contain higher amounts of health-boosting antioxidants. This study analyzed 343 peer-reviewed publications that showed “statistically significant and meaningful differences in composition between organic and non-organic crops/crop-based foods.” The researchers found that on average, organic crops have greater antioxidants concentrations and lower levels of cadmium, a harmful heavy metal. (23)
The cadmium finding in this study is significant to note. Cadmium is naturally found in soil and plants, but it is an extremely toxic metal that has been linked to serious health problems, which is why it’s great to see lower cadmium levels in organic crops. (24)
2. Environmental Impact
How is organic farming better for the environment? Unlike conventional farming, organic farming doesn’t use artificial and chemical-laden fertilizers and herbicides. This means that organic farms aren’t polluting the soil and nearby bodies of water with harmful and toxic chemicals. With each new year of crops, more and more fertilizer typically needs to be used to result in the same crop yield. Using artificial fertilizers and pesticides also has a negative impact on soil quality and makes erosion more likely. (Again, it’s important to note chemical-based agriculture is contributing to an increase in flooding.)
And farming chemicals aren’t just linked to diseases like cancer and developmental problems in humans, either. Neonicotinoid insecticides are being blamed for the worldwide collapse of bees; in addition, these same chemicals are also implicated massive songbird and bat die-offs, too.
Organic farming is much healthier for the environment since it does not employ chemical pesticides that are known to remain in the soil long term, continuously contaminating the food chain. (25) Organic farming also uses crop rotation which improves soil quality and prevents erosion. Plus, the employment of companion planting by organic farmers naturally controls pests and fosters the growth of plants. Overall, organic farming creates a healthy mutualistic atmosphere for its plants and makes a point to work with the natural environment rather than destroy it.
3. No GMOs
Certified organic farming means zero genetically modified food. The dangers of GMOs are not even fully known yet, since GMOs have not been around a very long time at all. So far, the studies endorsing the safety of GMOs appear to be conducted by the same biotechnology companies that are pushing these genetically engineered versions of natural foods. (26)
One of the major concerns with GMO foods is that the way in which they are created. GMO production causes DNA damage and creates mutations. Mutations in any living organism can cary the risk of negative health effects. For example, birth defects and cancer in humans are both caused by mutations to DNA. (27)
So far, animal research points to major concerns when it comes to the safety of GMOs. You may have seen the pictures of one study where the rats have tumors that are huge in proportion to their tiny bodies. These tumors were so huge that they blocked organ function. What were these rats eating? They were fed Monsanto’s genetically modified corn with or without Roundup herbicide. Both male and female rats suffered clear negative health effects, but the female rats seemed to experienced more negative effects from the GMO corn whether it was sprayed with Roundup or not. (28)
4. No Pesticides
Not only are chemical pesticides bad for the environment, but they’ve been shown to have significant health consequences on humans. Consuming food that contains pesticides causes pesticide buildup in our bodies. Many health problems have been linked to exposure to pesticide-based agrochemicals including memory loss, food allergies, diabetes, cancer, obesity, infertility and Parkinson’s Disease. Eating organic foods are a top way to reduce your pesticide exposure. (29)
According to the Pesticide Action Network of North America, reducing your exposure to pesticides can really make a difference. Research shows that pesticides linger in the body, and exposure begins as early as in the womb. Developing fetuses and children are especially vulnerable to pesticides because their bodies are still developing. DDT was a pesticide banned for agricultural use in the United States in 1972, but DDT breakdown products are still being found in the bodies of American citizens years later. (30)
Research conducted by USDA and published in 2016 found pesticide residues on 85 percent of tested food items. (31) The USDA has set “safe limits” on the pesticide reside amounts fruits and vegetables are allowed to retain, but are these small amounts really safe? Already, we have seen Monsanto’s Roundup linked to infertility and cancer.
5. Healthier for Farm Workers
Organic farming is also much healthier for any human beings (or animals) that are living and/or working on a farm. Workers on a conventional farm are regularly exposed to synthetic chemical pesticides and fertilizers. The entry point? Through inhalation or even through the skin. Adult farm workers may carry these chemicals home to their children on their clothes, leading to whole-family exposure. (32)
Farm workers have to work with pesticides so closely and so often. We’re talking about some really potent chemicals that are known to have immediate negative health effects, including eye irritation, rashes, dizziness, nausea, vomiting and headaches.
More serious, immediate effects have even been known to include seizures, loss of consciousness or death. Long-term health effects of pesticide exposure may include neurological disorders, birth defects, infertility and cancer. (33) Organic farming means a much healthier work environment for anyone working on a farm.
Future of Organic Farming — It’s Bright
Organic farming is only becoming more popular as time goes on. Unlike conventional farming, organic farming is a way to produce delicious and nutritious food without negatively impacting the growers, the land or the consumers.
Some farms choose to go a step beyond organic farming methods by also practicing biodynamic farming. These two classes of agriculture share a lot of common attributes. For starters, they both avoid synthetic chemicals and opt for natural fertilization and pest control methods. However, biodynamic farming follows even more stringent guidelines.
In biodynamic agriculture, the farm is seen as an organism in and of itself, meaning the soil, crops and animals are all one system. It’s a very holistic way of farming that emphasizes an ethical and ecological approach to food production. A biodynamic farmer operates his or her farm as its own tiny world. While an organic farmer may buy some organic seeds or organic feed for livestock, a biodynamic farmer will get those seeds or that feed from its own farm. Biodynamic farmers use scented flowers and herbal tea sprays to repel pests. They also harvest crops according to moon phases. (34) I’m sure you’re getting the picture of how biodynamic agriculture is very in touch with the earth.
Both biodynamic and organic farming continue to increase around the world as demand by consumers rises and more people realize the benefits of eating organic food. According to the United States Department of Agriculture: (35)
- Consumer demand for organically produced goods continues to show double-digit growth.
- Organic products are can be found in almost 20,000 natural food stores and nearly 3 out of 4 conventional grocery stores.
- Fresh vegetables and fruits have been the top selling category of organically grown food since the organic food industry started selling products more than 30 years ago.
- The sale of organic goods accounts for more than 4 percent of total U.S. food sales.
Final Thoughts
- Organic farming continues to become more and more popular — consumer demand is growing and there is no sign of it slowing down any time soon.
- Based on what we know so far about conventional farming’s use of chemical pesticides and fertilizers, sewage sludge, genetic modifications, radiation, degradation of soil, erosion of land and other offenses, it’s no wonder that more and more people are willing to spend a little more for organic food.
- I definitely know that it can get expensive to buy all organic, which is why the dirty dozen is so helpful in showing you how to prioritize your organic shopping picks.
- I also highly recommend choosing organic when it comes to meat and dairy products. If you have a local, certified organic farmer, that’s always a great first stop when you do your grocery shopping.











