
Suppose you're a straight woman thumbing through Tinder while waiting for the train, avoiding your homework, or bored at work. A picture of a deeply bronzed man pops up in your stream. How do you swipe? More interestingly, if someone asked you to explain why, how would you answer?
Say that it's this guy:
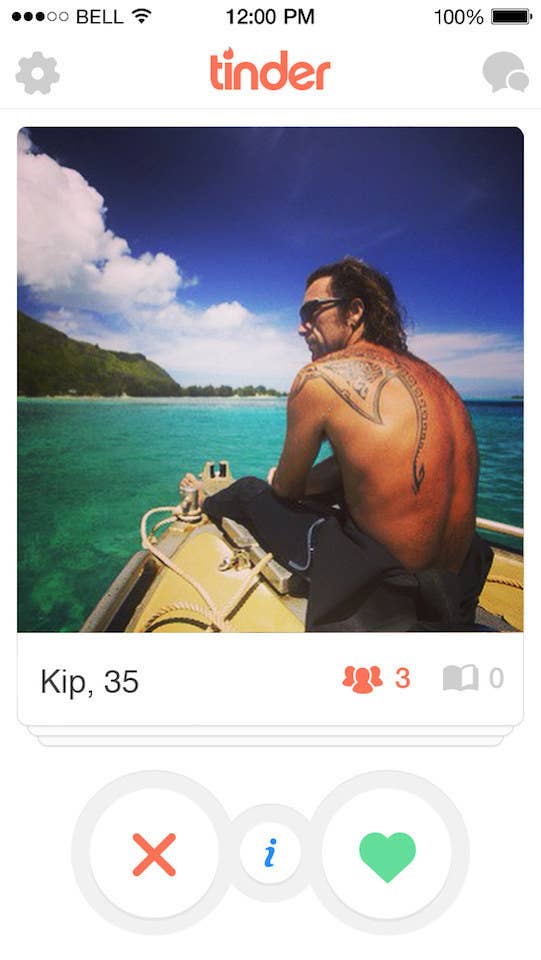
His location is exotic. He's doing something that requires a wetsuit. Chances are, he needed a good amount of money to do what he's doing in the place he's doing it. But the dark tan, large tattoo, long hair, and name like "Kip" indicate a lifestyle that is probably not that of an investment banker. You can't really see his face, but surprisingly that doesn't really matter because the overwhelming reason that hundreds of men and women who swiped "no" in a full-fledged Tinder simulation I unleashed on the internet had nothing to do with attractiveness. Instead, it had everything to do with the type of person Kip seemed to be:
"He probably calls himself a 'humanist' instead of a feminist and tries to impress people with how much he 'made friends with the natives' when he travels. Barf." —straight/white
"I love the tattoo, but he seems too skeezy in a way I can't put my finger on. Scuba is pretentious? Longer greasy hair?" —bi/Hapa/Japanese
"close call, but i hate his sunglasses and also i am imputing all sorts of things about him. like he probably says namaste to the barista at the coffee shop and has a profile picture of him with a bunch of african children" —bi/white
"Lol he's too old and it looks like the sea is his mistress already I can't compete with that." —straight/white
It's possible these respondents are "overthinking" their response to what, on the surface, is a very straightforward question: Am I attracted to this person or not? Indeed, some would argue that there's no reason to even explain: You can't argue with your genitals.
But maybe what we call the argument of one's genitals is, in truth, incredibly — and both consciously and subconsciously — influenced by the cultures in which we grow up as well as our distinct (and equally culturally influenced) ideas of what a "good couple" or "good relationship" would look like. Put differently, we swipe because someone's "hot," but we find someone "hot" based on unconscious codes of class, race, education level, religion, and corresponding interests embedded within the photos of their profile.
Essentially, we're constantly inventing narratives about the people who surround us — where he works, what he loves, whether our family would like him. And more than other dating services, which offer up comprehensive match dossiers, Tinder appears to encourage these narratives and crystallize the extrapolation process and package it into a five-second, low-stakes decision. We swipe, in other words, because of semiotics.
"Semiotics" is, quite simply, the study of signs. The field of semiotics tries to figure out how we come up with symbols — even as simple as the word in front of you — that stand in for a larger concept. Why does the word "lake" mean that massive blue watery thing? Or how does the stop sign, even without the word "stop," make everyone understand not to go forward?
But signs aren't always static in their meaning — it's all about context. Wearing a camouflage jacket can mean that you're in the military, a hunter, a punk, a redneck, a misogynist; having a shaved head, as a girl, can connote that you're a radical, a cancer survivor, or a lesbian.


I first noticed this "crystallizing" tendency in Tinder when a friend, let's call her Katie, starting playing it for fun, three beers in, at a bar. She was thumbing through prospective matches' profiles (usually comprising six Facebook pictures, authenticated Facebook age, and a brief bio line) for the table, yelling out her immediate reaction: too old, too manscaped, too short, too bald, too Jersey, HOT, too douchey, too finance-bro, too "ew," too hipster, too boring, too CrossFit, TOTALLY HOT.
Katie's performance is indicative of a larger truth: that most of the fun of checking people out isn't actually talking to them, but thinking about whether or not you'd talk to them and how. Katie was using Tinder at a bar, but instead of squinting across the room, she got to look at well-lit pictures of each potential match attempting to present his best self, seeing what phrase he uses to describe himself and a collection of ironic bon mots or general pronouncements ("no offense, but no crazies").
Tindering thus mimics the relationship of checking someone out on the street, in the classroom, or on the subway, but with the added tactile pleasure of physically swiping the rejects out of your field of vision (and your life). That's the real difference between Tinder and sites like OkCupid, Match, eHarmony, and J-Date: The end game on those sites is an actual date (and a lot of times marriage!); the end game on Tinder is the web version of a low-stakes bar conversation, which may or may not lead to a date or relationship.
Katie's verdicts were often based on obvious, glaring "facts" of the profile: A 5-foot-7 male was "too short." A 39-year-old guy was decidedly "too old" for Katie's 33 years. Another is bald; she decides him "too" much so. But other swipes relied upon more a more vague, albeit immediate, calculus. To be "too douchey" is to have a bad goatee, a shiny shirt, an unfortunate facial expression, or a certain type of sunglasses. "Too ew" could be any blend of traits that, to white, straight, middle-class Katie, read as repugnant.
But some judgments are too secret — and shameful — to say out loud, or even admit to ourselves. Katie never said "too not-white," "too poor," or "too uneducated." We cloak those judgments in language that generally circles the issue: "Nothing in common," "he wouldn't like me," "I can't see us together." Those statements aren't necessarily lies, but they're also not always full truths either — and often rely on overarching assumptions about what differences in race, class, education, and religion dictate not only in a relationship, but any interaction, romantic or otherwise.
After watching Katie and tinkering around on the app myself in a game-like fashion, I wanted to see if, relying on anonymity, I could get at the heart of the subconscious snap judgments behind each wipe. Why do we swipe the way we swipe? And are those assumptions "just human," or indicative of larger, enduring, and possibly destructive cultural divides?

Since there's no way to standardize Tinder's in-app selections for all respondents (and because using and publishing the real identities of strangers poses more than a few concerns), I decided to make my own, somewhat crude simulation. The first step: Scour stock images to find a broad array of profile "types."
The process proved fraught, as stock images for casually dressed black males, women over a size 4, and anyone who didn't fulfill stereotypical understandings of what male/female looks like require some unsettling search queries and yield clichéd and borderline racist results (try searching "curvy" or "fat," for example, and you get a sea of women looking very sad while looking at food or standing on scales).
I winnowed the profiles down to around 30 men and 30 women, processed them through Instagram filters to make them seem more like something someone might actually have on their account, and put them in standard Tinder profile frames. I picked approximate ages and came up with a mix of names — some of which were intended to complicate or amplify the mix of signs in the profile.


The result is an approximation, but not re-creation, of what Tinder is actually like. The goal was to correlate each participant's race, class, education, religion, and sexual preference to their swiping habits. For each Tinder "profile," regardless of whether they swiped yes or no, the user was prompted to answer "What race/religion/class and education level is this person?" And, if they swiped no, they were asked to write a brief explanation for "why," with a specific instruction not to simply note, "not attracted."
The survey circulated via Twitter, Facebook, email, and among friends, amassing 799 seemingly earnest respondents. It's not divided by the gender of the respondent, but by sexual preferences: If you desire men, you took the male simulation; if you desire women, you took the female one. If a participant identified as bisexual, he or she could take either.

The most swipeable woman — no matter if the user identified as straight, gay, queer, or bi — was Yasmin, with an 89% swipe-yes rate, a full 10% higher than her closest "competitor."
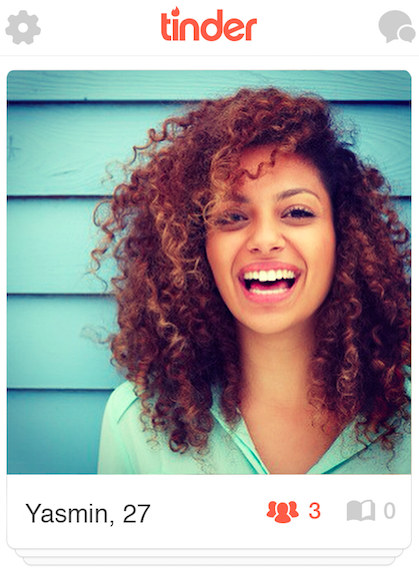

But why? She signified as middle-class (85% believed so); she seemed as if she had finished a four-year college degree or higher (83%). She looks Christian (42%), spiritual (20%), or agnostic/atheist (17%), and reads as either "mixed race" (48%) or black (40%).
Look closer at this image: Yasmin's teeth are white and straight and her skin is clear. Her shirt is nondescript, but doesn't read, at least from what we can see of it, as "cheap." The contrast between the shirt color and house in the background makes her look crisp and clean. Her overarching look is bourgeois, like a model in an issue of Real Simple.
Her eyes are "smizing," which makes it seem like she's actually happy, not just posing for the camera, all of which combines to create a feeling of "genuineness." Her hair seems only the slightest bit unruly — hey, she's not uptight! — but is also well-conditioned and cared for. She probably has means; she is content; she is educated; you will have something to talk to her about, and she will be pleasant.
But perhaps the most attractive thing about Yasmin, at least according to the simulation, is that her race is ambiguous. In his new book Dataclysm: Who We Are (When We Think No One's Looking), OkCupid co-founder and data scientist Christian Rudder asserts that "when you're looking at how two American strangers behave in a romantic context, race is the ultimate confounding factor." Working with star ratings and messaging data, Rudder found "two essential patterns" of male to female attraction: First, men tend to like women of the same race; second, men "don't like" black women.
So why, then, do Rudder's OkCupid findings not apply to Yasmin? It would appear she's not black enough. Just contrast Yasmin's profile with that of Lindsay, whom users read as unquestionably black (97%) and who received only a 43% swipe-yes rate.

Most respondents explained their rejection of Lindsay based on height and race, or, in one straight white male's words, because of "unconscious racism?" He continues: "Not that I don't find black women attractive — and not just the Beyoncés of the world, either — but this woman's aesthetic, which has definite racial and class markers, doesn't appeal to me at all."
Here, "aesthetic" seems to mean manipulated hair, more visible makeup, cluttered clothing, and a less-inviting facial expression. And those "definite racial and class markers" make users more likely to see her race. For Yasmin it's just the opposite: The absence of those racial and class markers make her race recede in importance (only two respondents, both straight white males, cited race as their reason for swiping no).
The same holds true for Xavier, who had the most swipeable male profile.
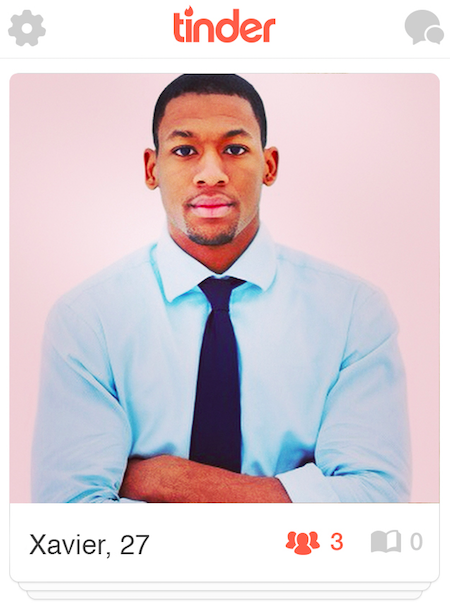

Xavier received a 79% overall yes rate — 10% higher than the closest "competitor." Ninety-five percent of users read him as black — a similar percentage to Lindsay — but users also perceived him as well-educated (95% percent thought he'd finished a four-year college or higher) and middle- or upper-class (74%/24%). The business attire makes him look professional, but not overly boastful; he looks directly at the camera and his arms are folded, which makes him seem direct. You could read his lack of smile as menacing, but the shirt and tie soften the effect.
The 21% who swiped "no" were bluntly concerned with race: "Not into black guys" (gay/white), "I think I might be racist" (straight/white), "interracial dating is not for me" (straight/white). Some pointed to race-specific traits without explicitly mentioning race: "his lips are way bigger than mine. I have thin lips and the thought of always kissing gimungous [sic] lips is scary to me," wrote one bi/white user.
Then there's the cultural extrapolation: "Man, he's pretty. And he seems really engaged and confident. But I can't see him at the next big half Polish, half French, all judgmental family picnic" (white/straight).
But why was Xavier rejected for his race more than Yasmin? Both read as middle-class and educated; both appear clean-cut in their pictures. But Xavier reads as "more" black and he isn't smiling; black men read, stereotypically, as more threatening than black women. Now, that's all racist and speculative, but it also seems to mimic how our racist and speculative subconsciousness functions in the split second it takes to swipe a Tinder profile.

Here's the religious breakdown of the simulation participants compared to national statistics from the 2012 Census:
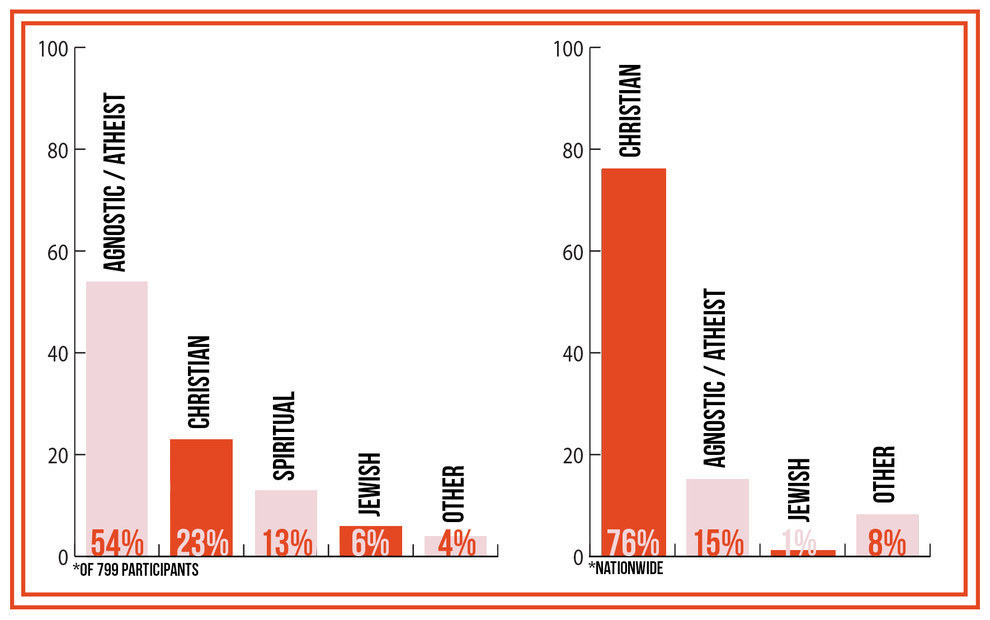
The discrepancy is fairly easy to explain — the mostly twenty- and thirtysomethings who took the simulation are less religious than their parents and grandparents. Participants were willing, however, to assign religious beliefs to the profiles they rejected.
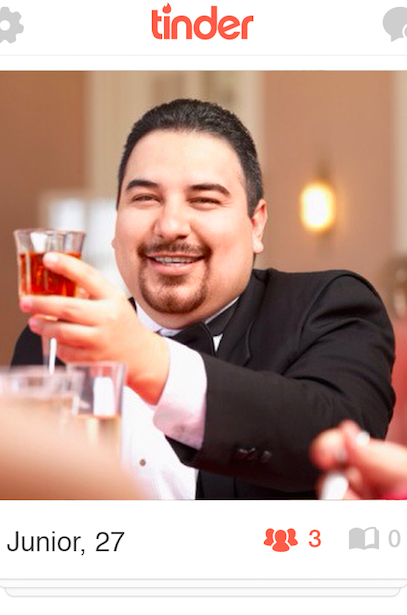



Take, for example, Junior, who garnered a paltry 7% swipe-yes rate. The stated reasons for rejecting Junior were variations on "he seems old school, like he'd be really patronizing to women" (bi/white) and "He's overweight/doesn't seem athletic" (straight/Asian). Eighty-one percent of users also read him as Christian — which could be correlated to the 70% who believed he was Hispanic, an ethnicity often associated with Catholicism. (Importantly, no respondent cited religion or ethnicity as their reason for swiping "no" on Junior.)
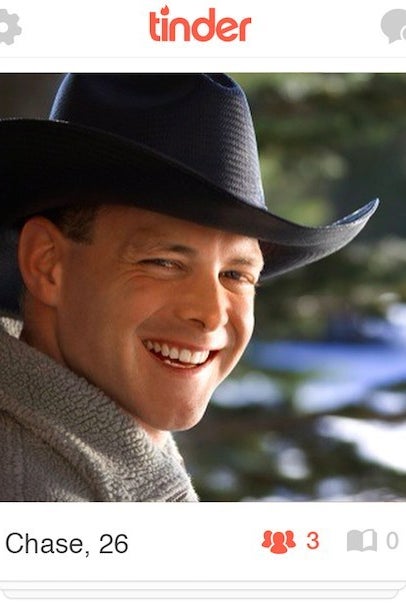
Same with Jimmy, who also pulled a 7% swipe-yes rate. Users didn't like his truck and read him as "Southern" and working-class (84%). Seventy-five percent of users believed he was Christian, despite no physical indications of religiosity. A similar yoking happened with Chase, a man with a nice smile and a cowboy hat, whom 86% of users read as Christian.
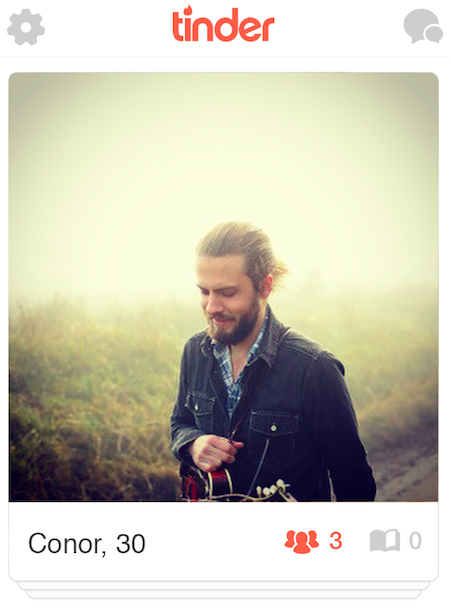

By contrast, here's Conor — who received a 56% swipe-yes rate. He's holding a mandolin, he has a beard and long hair, and the reasons for rejection usually had something to do with said beard and the lifestyle it connoted. But only 10% of users thought he was Christian — while 60% thought he was atheist/agnostic, and 20% believed he was spiritual. Even though, like Jimmy and Chase, he's photographed outdoors, certain hipster signifiers (not looking at the camera, long hair, mandolin) negate that reading.

When a profile includes obvious signifiers of religious belief, however, the reading process becomes more complicated. Thirty percent swiped "yes" on Kate, and despite signifiers that many interpreted as hipster, many signaled the cross around her neck as indicative of Christianity. A white, bisexual respondent wrote, "I don't date people serious about their religion"; a gay Hispanic woman called the cross "a huge turn off"; and one who identified as mixed race and straight thought she seemed "a bit arts-y and sanctimonious (spiritual)."
That said, perceived religiousness is not an automatic "no." Take Johanna, who had an overall yes rate of 64%:
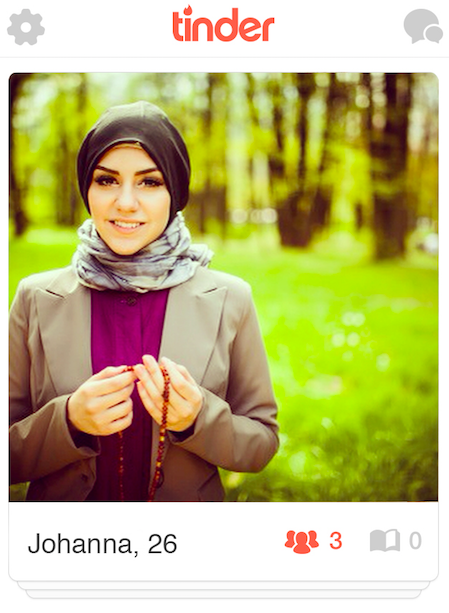

Eighty-seven percent of users read her as Muslim. The reasons for swiping "no" were almost entirely contingent on her perceived religion and its cultural extrapolations: A white male said, "I wouldn't want to deal with cultural differences in the bedroom"; a gay Hispanic user said, "I have no patience for religious people. She's hot, but sadly religion is the biggest turn off for me."
Overall, however, Johanna had an excellent Tinder swipe-yes rate (58% of straight men, 75% of bi men or women, and 78% of gay women).
Johanna signifies as religious, but unlike Jimmy, Junior, or Conor, she also signifies as middle- or upper-class (71%/26%) and college- or graduate school-educated (64%/26%). Like Chase and Jimmy, she's photographed outside, but she wears a women's suit jacket. Even those who swiped "no" on her profile for religious reasons conceded that "she is very cute" and "she's hot."
Religion — even religion that would likely preclude a successful relationship — seems to matter less when the subject seems to belong to a higher class and educational level (especially if that subject is gorgeous).

Let's examine Dave, one of the lowest-scoring male profiles. It's an ambiguous profile — there are four men, and no sign as to which one is "Dave" — but that's also the case with many Tinder profiles. But the rage directed at Dave wasn't primarily due to the inclusion of his friends in the shot. Rather, it was his apparent privilege — communicated via the golf course, the uniform whiteness of himself and his friends, and the apparent gall to use a golfing photo as one's profile picture — that led respondents to say the following.
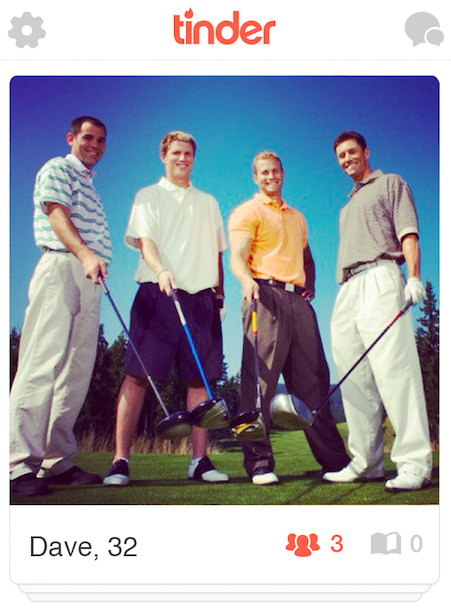

It was bad. Like, really bad:
"NO NEVER IN A MILLION GODDAMN YEARS. This privileged fuck, first of all, which one is he? Does it even matter? No, because all polo shirts are interchangeable." —bi/white
For the record, not interested in any of those white frat boys in that picture." —straight/Asian
"I can't tell which of these four dudes he is, but I don't want to date The Man." —bi/white
"they all look like finance bros which might be the worst subcategory of bro." —straight/white
"Not sure which one of these guys is Dave, but that doesn't matter, because they all seem like Republican d-bags. Also: Pleated khakis? No." —gay/white
"SO WHITE" —queer/Asian
"golf. overabundance of white dudes. who is Dave? Dave is legion. a legion of golf-playing white dude demons." —pansexual/white
Dave scanned as well-educated (71% believed he'd finished college; 20% thought he'd finished grad school) and definitively upper-class (73% believed as much, the highest of any profile). But unlike other white men of higher class and education level, users also overwhelmingly read him as Christian: a whopping 79%. (Compare with Kieran, another white, well-educated male, whom 64% of users read as agnostic/atheist.) Respondents read Dave's hobby and whiteness as indicative not only of wealthy, but Conservatism — which is often associated, explicitly and implicitly, with Christianity.
Dave demonstrates how Tinder's lack of information forces assumptions from its swipers, which is is a perfect example of what makes Tinder so unique and perfect for this experiment. On OkCupid or Match, there would be clear markers of one's political views. But on Tinder, you have only the presence of a pair of pleated khaki pants to tell you if the person is, say, conservative, "a douche," and thus unattractive.

No one wants to believe their attractions are racist, or classist, or otherwise discriminatory. We use elaborate phrasing to cover it up or explain it away, but it's still there, even if not always to the profile's detriment. The fact that the two profiles with the highest swipe-yes rate were both people of color seems to suggest something about shifting understandings about attractiveness, which makes sense given our respondents (overwhelmingly middle-class, largely white, and mostly urban and suburban denizens of the internet).
But "what we find attractive" appears to be far less about someone's face and far more about the signs that surround that face. Think, for example, if a woman like Marit, pictured below, had the cheap highlights and unfixed teeth and name of Crystal?
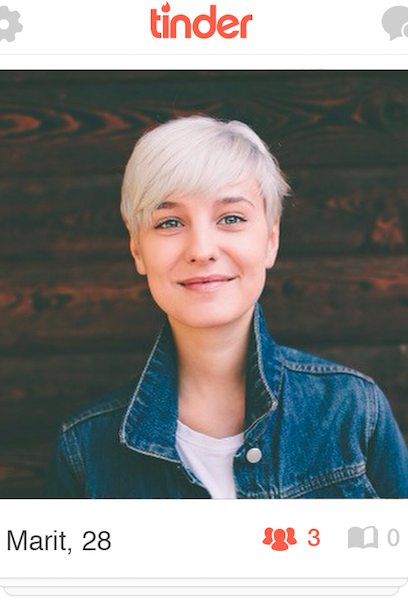
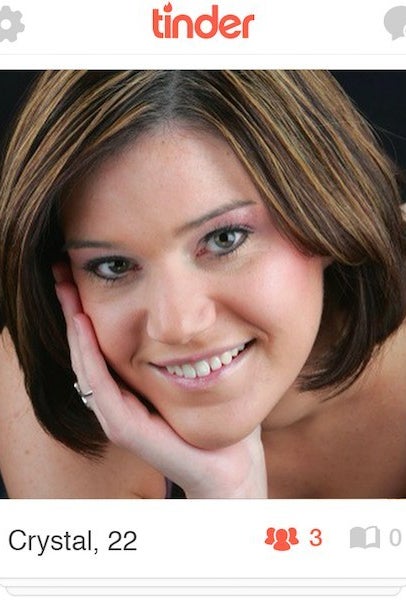


Though still anecdotal, Tinder rejection in this simulation appears to be more about class than race or religion. If a user self-identified as upper-middle-class and identified the male profile before him or her as "working-class," that user swiped "yes" only 13% of the time; if they identified themselves as lower-middle-class, the swipe rate rose only slightly to 17%.
If those same users identified the profile before them as middle-class, that number rose to 36% and 39%, respectively. The same trend held true when judging female profiles: If the user identified as upper-middle-class and identified a profile as working-class, the yes rate was 26% — compared with 52% if they identified a profile as middle-class.
Whatever the signs that made someone think that a profile was working-class — McKenzie's fishing pole, Renee's dye job and pool pose, Ricky's tattoos and piercings, John's tank top, Toby's camo, Jimmy's truck — the swipe rates plummeted.
Which isn't to suggest that poor people are ugly. The vast majority of explanations for the no swipes on all of the above profiles pointed to a perceived lack of common interests: "we'd have nothing to talk about," "I don't think our politics would mix," "nothing in common." Sometimes those assumptions stem from depicted activities — fishing, body modifications — but some are just the way the mind runs wild with class, weaving the narrative that a working-class person probably doesn't read books for pleasure, or enjoy art cinema, or seek out microbrews, or go on hikes the way a bourgeois, middle-class person does.
Now, the results of a small sample-size Tinder simulation doesn't mean that we're all destined to marry within only our own classes. Data on the tendency to marry within one's class is difficult to come by, but if relying on education level as an (imperfect) proxy for class, then the rate has decreased dramatically over the 50 years. Even as more and more people marry "across" lines of race and religion, fewer and fewer are willing to cross the education/class line.
Tinder is by no means the cause of this decline. It simply encourages and quietly normalizes the assumptions that undergird it. The Tinderspeak of "we'd have nothing in common," taken to its natural extension, bolsters and reifies the idea of "two Americas" with distinct values and worldviews, two discrete factions with little impetus to support that which doesn't necessarily personally affect us or our class.
It's not as if race and religion aren't still mitigating factors in our decisions about whom we find attractive, with whom we emphasize, or for whom we feel compassion. Race and religion do matter (and might always), but almost only when they intersect with a class identity that isn't our own.
Ultimately, this admittedly un-randomized sample seems to suggest that the raw idea of attraction — that knee-jerk "thinking from the genitals" decision — has less to do with our unmentionable parts and much more to do with a combination of our deepest subconscious biases and with our most overt and uncharitable personal politics. And if that's the case, it's no doubt the reason why Tinder is so popular, addictive, and ultimately insidious.
