Liquid metal brings soft robotics a step closer
Scientists have invented a way to morph liquid metal into physical shapes.
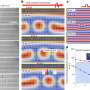
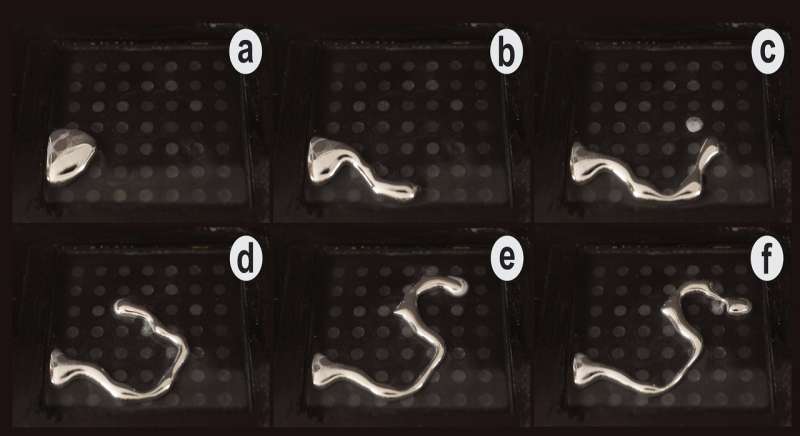
Researchers at the University of Sussex and Swansea University have applied electrical charges to manipulate liquid metal into 2D shapes such as letters and a heart.
The team says the findings represent an "extremely promising" new class of materials that can be programmed to seamlessly change shape. This open up new possibilities in 'soft robotics' and shape-changing displays, the researcher say.
While the invention might bring to mind the film Terminator 2, in which the title character morphs out of a pool of liquid metal, the creation of 3D shapes is still some way off. More immediate applications could include reprogrammable circuit boards and conductive ink.
Yutaka Tokuda, the Research Associate working on this project at the University of Sussex, says: "This is a new class of programmable materials in a liquid state which can dynamically transform from a simple droplet shape to many other complex geometry in a controllable manner.
"While this work is in its early stages, the compelling evidence of detailed 2D control of liquid metals excites us to explore more potential applications in computer graphics, smart electronics, soft robotics and flexible displays."
The electric fields used to shape the liquid are created by a computer, meaning that the position and shape of the liquid metal can be programmed and controlled dynamically.
Professor Sriram Subramanian, head of the INTERACT Lab at the University of Sussex, said: "Liquid metals are an extremely promising class of materials for deformable applications; their unique properties include voltage-controlled surface tension, high liquid-state conductivity and liquid-solid phase transition at room temperature.
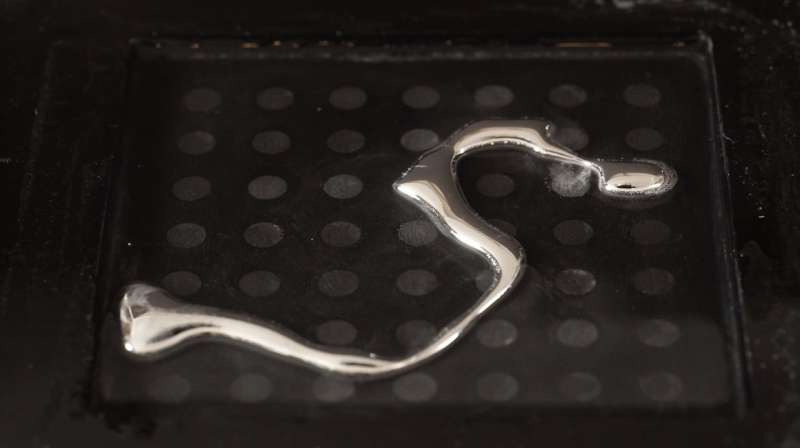

"One of the long-term visions of us and many other researchers is to change the physical shape, appearance and functionality of any object through digital control to create intelligent, dexterous and useful objects that exceed the functionality of any current display or robot."
More information: Yutaka Tokuda et al, Programmable Liquid Matter, Proceedings of the Interactive Surfaces and Spaces on ZZZ - ISS '17 (2017). DOI: 10.1145/3132272.3134132
Provided by University of Sussex