15 things that are stopping your site from ranking well in Google and how to fix them
How much can a search engine change in a year? If it’s Google, the answer is a lot. While some good old search engine optimisation (SEO) practices might have worked in the past, Google’s constant tweaks to its algorithms can actually turn your efforts into web page death sentences if you’re not careful.
If you’re in the wrong and it’s affecting your rankings, you probably want to do something about it. To get you on the right track, we’ll walk you through 15 things that you’re doing that might be preventing your site from ranking well in Google’s search engine results and how you can fix them.
We’ve split them into three categories, taking into account Google’s top ranking factors
A. Backlinks
B. Content
C. RankBrain
Make sure you review and optimise your website for these three key factors, otherwise you risk never ranking well in Google.
A. Backlinks
A few years ago, Google loved and encouraged the building of backlinks. A link back used to mean that your site was recommended and recognised as a trustworthy source for information.
But when spammers started abusing guest blogging and backlink tactics to mislead the search engine into believing that their sites were of high authority, Google reworked the system. They started penalising all sites that were getting or paying for tens or hundreds of irrelevant backlinks in a very short period of time.
This means that now any link that looks unnatural can lead to your website being penalised. The focus has shifted from getting as many links as possible to earning valuable links and recommendations.
So what type of backlinks can harm your ranks?
1. Branded links for EMD websites
When users link to your site, the chances are they will add the link as your brand name rather than a product name. That’s great. But here’s the thing: if your brand name is the same as your product name there’s a good chance you will get product related links instead of branded ones. This can lead to a penalty.
An example of this is PSD2HTML. Its brand name is“PSD2HTML” while their product is “PSD to HTML”. The site was penalised by Google because users were creating branded backlinks as “PSD to HTML” as this is what they thought the site was called. Because this was the same as the product name, Google penalised the site because the search engine thought PSD2HTML had been acquiring product links against its rules, when in fact the links were entirely legitimate. You can read the case study on this and how they managed to remove the penalty in a post on Moz.
What can you do? Avoid using a domain name that is the same as a keyword or phrase someone would use to search for the product you sell, know as exact match domains (EMD), and go with a branded name for your domain.
2. Reviews in exchange for products or services
In April, Google started penalising bloggers who were writing product reviews in return for free products or services. Now, the chances of your website being penalised for having a paid review on a blog that got a Google penalty are slim. However, what’s important to keep in mind is the fact that that backlink loses value when the blog gets penalised. This means that your website will lose the support of that backlink and, as a result, your ranking can drop.
What can you do? The best piece of advice we can give you is to not waste your time and resources on building backlinks through paid reviews. Even if you’re just getting started with your website and want to get it to rank high quickly, this is not the way to go as it can lead to a Google penalty. Removing a penalty can set you back months of hard work, and fixing it can take longer than it would take to get your rankings up the proper way.
3. Guest blogging
Most site owners have used guest blogging as a technique to quickly build lots of links to their site instead of to share useful information with interested people. As site owners were only doing this to get some backlinks, Google decided guest blogging was no longer helping to generate legit backlinks. As a result, Google started to devalue these links and even penalised some sites that had built a lot of links through guest blogging.
So these days trying to build backlinks by guest blogging on just any site that’ll take you can be a waste of time, and it can also get you a penalty for unnatural links.
But what if you have a guest blogging opportunity from another website in your niche and they invite you to write a post because they truly believe you are an expert in your field? Should you say no just because you don’t want to risk a Google penalty. That’s just silly.
You’ll first need to do your research to ensure that the site you’re planning on writing for is trustworthy. If it is, then go ahead and write a great piece packed with useful information. Just make sure your content is relevant to that website and that the audience you’re addressing will benefit from reading your article.
4. I link to you – you link to me
It’s not uncommon for small businesses to form relationships and to help each other out by linking between their sites in order to enhance SEO and click-through traffic. While this isn’t usually problematic, it can cause issues if the businesses aren’t in any way related. Think about it this way: if you think it doesn’t make sense to link to a site, Google will know it too. Those good intentions can end up hurting both sites so you might want to think twice before linking to a site that isn’t relevant to yours.
This is what happened to a major online retailer of greeting cards that entered into a relationship with a major brick-and-mortar retailer. The brick-and-mortar retailer placed a footer link to the online retailer site on every page of their site (a total of 16 million links!). It didn’t take long for the online retailer to get penalised for having a suspicious link profile. Read more about it in this post.
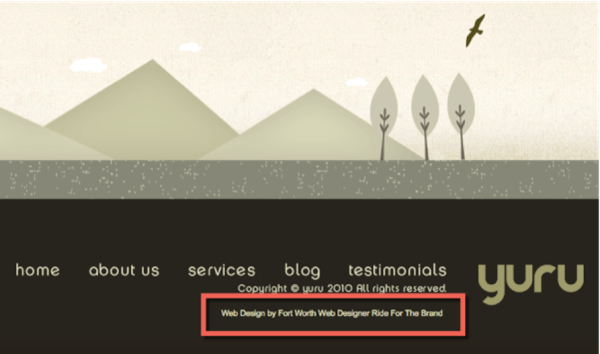
Another example, and you’ve probably seen this many times, is having a footer link to the web designer’s site like in the example below:
It’s a common technique for designers to add a signature link to the sites they’ve helped build. But if your site is about NGOs or gardening, how is it relevant to link to a web designer’s site from every single page on your site?
5. Directories
If you’re just getting started online, you’re probably considering listing your website in different directories to increase your chances of getting found online by potential customers. Take some time to research the directories that you’d like to submit your site to. So many of them are spammy or don’t get any visibility themselves so what would be the point in getting listed? You’ll only end up with a backlink from a worthless site.
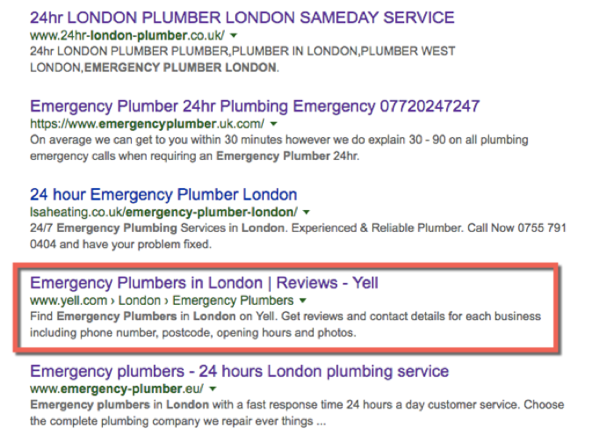
If you do find a directory that’s relevant for your business, make sure it shows up in the search results for your business’ niche. For example, a search on Google for “emergency plumber London” showed the Yell directory on the first results page:
This means that this directory is a place you might consider listing your plumbing business on.
Bottom line, if you want to list your website in directories, make sure the ones you choose are either well-known ones like Google My Business and Yelp, or others that are relevant to your business as well as visible in the search results. You can find a pretty comprehensive list of directories here, with the biggest highlighted in red.
B. Content
6. Avoid duplicate content
Every piece of content you write needs to be unique, weather you publish it on your site, on your blog or elsewhere on the web. Don’t just change a few words in your content and the publish it elsewhere to save time and under no circumstances should you use software or tools to do that for you content. Search engines nowadays are smart and are able to tell whether a piece of content is original or a spinoff. And you don’t want to risk getting a penalty just because you’re lazy or you lack the time to create original content, don’t you?
But even if you’ve made the effort to create all your content from scratch, in some cases you might not even know that you have duplicate content issues. Did you know that duplicate content can also be created by your content management system?
To prevent this from happening, make sure your website either redirects or has canonical tags for its www and non-www versions. The same goes for HTTP and HTTPs if your website is secured. So what you need to do is set your preferred domain, whether with or without www, http or https, and implement 301 redirects for all other versions of your URL. This will redirect visitors to your preferred domain and will also prevent duplicate content issues. It doesn’t matter which URL version you choose as long as you are consistent with it. Here’s how to do a 301 redirect on any platform. Alternatively, if this sounds too daunting, your web designer should be able to do it for you.
7. Losing authority by deleting pages
If you find yourself in a situation where you think a certain page on your site is no longer useful or necessary, don’t rush to delete it as you can lose authority. For example, if one of your products is out of stock or if you’re no longer providing a specific service, don’t delete those pages completely. Instead add a message that lets users know that that product is out of stock now but that you’ll restock soon; or that the service in question is temporarily unavailable.
If you decide to no longer sell that product or service, you can always redirect the page to another page with a related product or service so that users can still find a similar solution.
If you stop selling a product completely, you can permanently redirect the page to that product’s category page. Even if users can’t find that specific product anymore, they can at least browse through similar products that you have available.
We recommend using the same strategy for your old blog posts. Don’t just delete them. Instead permanently redirect them to newer posts on the same subject or to the category they’re part of.
From the moment you publish a page it starts gaining authority from backlinks and internal links. If you delete that page, you also delete that authority from your site. A 301 redirect can help you to pass most of that authority to another page. Just make sure that the page you redirect the old page to is relevant. If it’s not, Google can simply decide not to pass any of the authority even if you implement the redirect correctly.
But what if you have no similar relevant pages to redirect to? In this case you can return a 404 page with links back to other important pages on your site that users might be interested in. This way you can ensure visitors don’t leave your site immediately after they hit a not found page.
8. Heavy exact match interlinking or no interlinking
Internal links are vital to helping search engines understand which are the most important pages on your site and the relationship between your web pages.
Product pages usually get linked the most because they’re commonly placed in the menu and footer. However, if you only provide services or if there are more important pages that you want to make easy to find, make sure they’re included in your site’s navigation.
Now, since you can’t add all the pages on your site to your menu, at least ensure that secondary pages get linked to from your product pages.
Visitors on your site should be able to access all your pages. If a page is not linked to from any other page, that’s called an “island page”. While these types of pages can still rank organically, users won’t be able to find them. What’s worse, they can attract a penalty so make sure that every page of your site can be found through another page.
An important thing to consider here is the anchor text, and here’s what you should keep in mind:
- Diversify your anchor texts. Instead of using the same anchor text every time to link to a specific page, try to diversity it. Besides menus and footers, where the anchor text stays the same, try to come up with different copy for the anchor texts inside the body content.
- Make it descriptive. If you take it out of context, users should still be able to understand what happens or which page they’re being redirected to when they click the link. For example, an anchor text like “[product name]” is generic and is not as descriptive as “See our full range of [product name]” or “Compare prices for [product name]”.
9. Page speed
You probably know by now just how important it is for your site to load quickly. Page speed not only has an impact on your rankings, being one of Google’s confirmed ranking factors, but also on whether your visitors stay on your site for longer than a few seconds. So if your site is slow, you’re not only losing visitors from impatience but also rankings in the search engines. Yikes!
Go to Google’s PageSpeed Insights tool to check and see how fast your site is loading. If you have a WordPress site and you’re having issues or want to maximise your site’s speed, check out our guide on how to speed up your WordPress site.
10. How your content looks on different devices
Google is separating the desktop index from the mobile index. This means that while the desktop of your website can perform well for users using a PC, it might not have an organic presence for users visiting your site from a mobile device.
Why is this important? As Google’s Zero Moment of Truth ebook says, mobile is “not ‘the wave of the future’ any more — it’s right now”.
With the increasing number of people using mobile devices to browse and shop online and with Google giving more priority to mobile friendly sites, if your site isn’t responsive, you risk being left behind.
There’s no time like the present to test and see whether your site displays properly on mobile devices. Go to Google’s test tool, enter your site’s URL or the URL of a specific web page and see if you pass the test.
For more useful information check out our posts to learn more about what makes a mobile-friendly site, how to get one yourself and what mistakes to avoid when designing your site:
C. RankBrain
RankBrain is the third most important signal out of the hundreds that go into Google’s algorithm. It’s the machine-learning artificial intelligence system that Google uses to process and refine its search results. We’ve written a comprehensive post about it, what it is and what RankBrain means for your small business site, so make sure you read it if you want to learn more.
The purpose of RankBrain is to help the search engine giant better understand the huge amount of queries it receives every day and to provide users with the most relevant results to their queries.
So if you want to rank higher, here’s what you should stop doing immediately:
11. Writing spammy, keyword-stuffed content
Since Rankbrain understands intent, stuffing your content with the same keywords over and over again is the recipe for failure. This tactic might have worked in the past but not anymore.
Great, properly optimised content is no longer about using the exact keywords and phrases that users search for, whether they’re grammatically correct or not. User searches have evolved to more complex queries. In other words, write for your users first, and then for search engines.
12. Not answering users’ questions
Try to put yourself in your visitors’ shoes and think about how they would search to find your products – which words they’d use, what questions they’d ask, what information they’d be looking for. Use these insights and create content that answers their questions and gives them the exact information they’re searching for. Rankbrain tries to match even the most complicated searches with the most relevant content so make sure you have it ready for users to find.
13. Putting it all on one page
Pages with content that covers too many topics will never rank high in the search results. Instead, try to focus each page on a specific topic and add as much useful information as you can. This not only ensures that users will find the information they’re looking for, but you’ll also be covering more related terms that are relevant to your topic, thus helping your page to rank higher in Google’s SERPs.
14. Not being original
If you want your content to stand out and if you want to become an authority in your field you need to give more than your competitors. You’ll never be regarded as an expert if all you do is regurgitate or rewrite other people’s content.
When writing content, whether it’s for a product page, an infographic or a blog post, you need to be original to set yourself apart from the competition. Find a different angle when writing an article or focus on something unique that you offer that no one else does when promoting your products or services. It’s not easy but it’s the surest way to success.
Proper SEO
15. Careful who you hire to do your SEO for you
Things have changed dramatically over the past few years in terms of SEO. If all this seems too complicated or time-consuming, and you decide to hire an SEO agency or professional to take care of your SEO strategy for you, make sure you do your research to ensure they know what they’re doing.
Watch our webinar to learn what questions to ask your SEO agency to make sure they’re doing the things they should be doing. We also recommend reading our post to see what are the red flags and how to avoid hiring the wrong SEO firm.
Wrapping up
These are some of the most important things that can prevent your site from ranking high in Google’s search engine results. Your next step? Review your site closely and see what you can implement from our (hopefully) useful advice in order to get your site better visibility in the search engine results.